Anatomy of Stem
Anatomy of Stem: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Anatomy of Dicot Stem, Anatomy of Monocot Stem, Anatomy of Stem, Vascular Bundle of Monocot Stem and, Vascular Bundles of Dicot Stem
Important Questions on Anatomy of Stem
Choose the incorrect statement:
Sclerenchymatous sheath is present in vascular bundles of
Endodermis of dicot stem is also called
Conjoint vascular bundle is present in
Endodermis of dicot stem is called as:
‘’-shaped arrangement of xylem vessels is seen in
In a typical dicot plant, the vascular cambium of roots differs from the vascular cambium of stems in
The following diagram shows the TS of dicot stem, certain parts have been indicated by and Select the right answer in which these alphabets have been correctly matched with the parts which they indicate
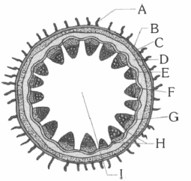
The following diagrams shows the cross-section of the vascular bundle of monocot stem given aside, different parts have been indicated by alphabets; choose the option in which these alphabets have been correctly matched with the parts which they indicate
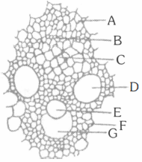
T.S. of stem of Cucurbita can be identified from the T.S. of sunflower stem by the presence of
Generally hypodermis in monocots is composed of
Vascular bundles are scattered in
Vascular bundles are derived from (originate from)
The balloon like outgrowth of parenchyma in the lumen of a vessel is known as
Dicot stem differs from monocot stem in lacking all, except
Identify the given figure and select the incorrect option.

The following anatomical features are related with
(a) Presence of sclerenchymatous hypodermis.
(b) Presence of water-containing cavities within vascular bundles.
(c) Presence of atactostele.
Hypodermis is collenchymatous for mechanical strength in
